HEAD INJURY - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
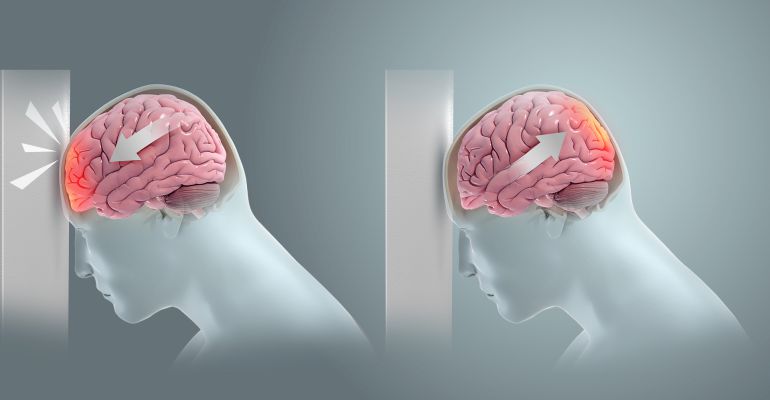
Traumatic brain injury usually results from a violent blow or jolt to the head or body. An object that goes through brain tissue, such as a bullet or shattered piece of skull, also can cause traumatic brain injury.
Mild traumatic brain injury may affect your brain cells temporarily. More-serious traumatic brain injury can result in bruising, torn tissues, bleeding and other physical damage to the brain. These injuries can result in long-term complications or death.
Physical symptoms such as:
• Headache
• Nausea or vomiting
• Fatigue or drowsiness
• Problems with speech
• Dizziness or loss of balance
Sensory symptoms such as:
• Sensory problems, such as blurred vision, ringing in ears, bad taste in mouth or changes in the ability to smell
• Sensitivity to light or sound
Cognitive, behavioural or mental symptoms such as:
• Loss of consciousness for a few seconds to a few minutes
• No loss of consciousness, but a state of being dazed, confused or disoriented
• Memory or concentration problems
• Mood changes or mood swings
• Feeling depressed or anxious
• Difficulty sleeping
• Sleeping more than usual
Symptoms like headache, weakness, confusion, and paralysis (particularly on one side of your body), appear suddenly as the buildup of blood puts pressure on the brain and interferes with its oxygen supply. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
